 Leetcode题解(8)- 2018 力扣 Leetcode CN 高频题汇总 part 4 哈希与映射、树
Leetcode题解(8)- 2018 力扣 Leetcode CN 高频题汇总 part 4 哈希与映射、树
# 哈希与映射
# Excel表列序号
Leetcode 171题,进制转换。已经做过啦,参考这里 (opens new window)
# 四数相加 II
Leetcode 454题。
# 问题
给定四个包含整数的数组列表 A , B , C , D ,计算有多少个元组 (i, j, k, l) ,使得 A[i] + B[j] + C[k] + D[l] = 0。
为了使问题简单化,所有的 A, B, C, D 具有相同的长度 N,且 0 ≤ N ≤ 500 。所有整数的范围在 -2的28次方 到 2的28次方减1 之间,最终结果不会超过 2的31减 1 。
# 思路
最暴力的是穷举四个列表,这样复杂度要o(n^4)了,怕是根本不可以。 可行的一种做法是,先两层循环,将AB相加,并将值作为key,次数作为value计入hashmap中,然后两层循环将cd相加,并将其值乘以-1然后在刚才的hashmap中找有没有对应的值,如果有则说明找到了四者之和为0的,count累计即可。这样的复杂度是o(n^2),相对小很多了。
# 代码
class Solution(object):
def fourSumCount(self, A, B, C, D):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:type B: List[int]
:type C: List[int]
:type D: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
counter = {}
result = 0
for a in A:
for b in B:
s = a + b
if s in counter:
counter[s] += 1
else:
counter[s] = 1
for c in C:
for d in D:
s = -1 * (c + d)
if s in counter:
result += counter[s]
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素
Leetcode 380 题
# 问题
设计一个支持在平均 时间复杂度 O(1) 下,执行以下操作的数据结构。
insert(val):当元素 val 不存在时,向集合中插入该项。 remove(val):元素 val 存在时,从集合中移除该项。 getRandom:随机返回现有集合中的一项。每个元素应该有相同的概率被返回。
// 初始化一个空的集合。
RandomizedSet randomSet = new RandomizedSet();
// 向集合中插入 1 。返回 true 表示 1 被成功地插入。
randomSet.insert(1);
// 返回 false ,表示集合中不存在 2 。
randomSet.remove(2);
// 向集合中插入 2 。返回 true 。集合现在包含 [1,2] 。
randomSet.insert(2);
// getRandom 应随机返回 1 或 2 。
randomSet.getRandom();
// 从集合中移除 1 ,返回 true 。集合现在包含 [2] 。
randomSet.remove(1);
// 2 已在集合中,所以返回 false 。
randomSet.insert(2);
// 由于 2 是集合中唯一的数字,getRandom 总是返回 2 。
randomSet.getRandom();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 思路
emmm看起来挺复杂但我发现很多题解都是直接拿库函数set和random写了一个hhhhh,直接调包这就简单多了
# 代码
import random
class RandomizedSet(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.data = set()
def insert(self, val):
"""
Inserts a value to the set. Returns true if the set did not already contain the specified element.
:type val: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if val not in self.data:
self.data.add(val)
return True
return False
def remove(self, val):
"""
Removes a value from the set. Returns true if the set contained the specified element.
:type val: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if val in self.data:
self.data.remove(val)
return True
return False
def getRandom(self):
"""
Get a random element from the set.
:rtype: int
"""
return random.choice(list(self.data))
# Your RandomizedSet object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = RandomizedSet()
# param_1 = obj.insert(val)
# param_2 = obj.remove(val)
# param_3 = obj.getRandom()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# 树
# 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
Leetcode 230题
# 问题
给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数 kthSmallest 来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
# 思路
二叉搜索树的特点是左子树上的所有节点都小于根,右子树则都大于根,对二叉搜索树进行中序遍历,就可以得到一个有序的序列。这里也不需要完全进行一次中序遍历,标记到第k个时即可终止返回。
# 代码
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.cnt = 0
self.res = None
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
if not root:
return
self.kthSmallest(root.left, k)
self.cnt += 1
if self.cnt == k:
self.res = root.val
else:
self.kthSmallest(root.right, k)
return self.res
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 二叉树的最近公共祖先
Leetcode 236 题
# 问题
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 在树中所处的深度尽可能大,(尽可能靠近树底)(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
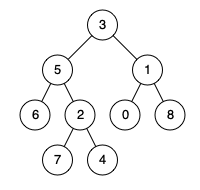
例如上图中,5和1,答案为3;如果是5和4,答案为5(节点也可以是自己的祖先)
# 思路
一种思路是通过添加额外的信息记录来实现,比如说我们可以把树遍历一遍,并且记下每个节点的祖先,这样p的祖先的祖先的祖先的祖先是一个序列,q的是一个序列,相当于找两个序列最近的交点,就是最近的公共祖先了。
另外一种思路是递归来做,拿到一个节点root,如果root等于null或者p或者q直接返回,否则在其左右子树中查找pq,如果pq都不在说明找不到;如果pq同在一侧,则继续在这 一侧为root来找;如果pq分别在两侧,则这个节点就是最近共给实现。
# 代码
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not root or root.val == p.val or root.val == q.val:
return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if not left and not right:
return None
elif left and right:
return root
elif left:
return left
else:
return right
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
Leetcode 297题,也是剑指offer中出现过的 (opens new window)。
# 问题
实现二叉树的序列化/反序列化
# 思路
之前剑指offer中的思路是通过前序遍历来做,递归前序遍历二叉树,对每个节点的孩子如果遇到空就以#来代替,最终得到一个字符串。读取字符串,当前字符作为根,下一个字符作为当前的左孩子,依此递归进行前序遍历,恢复树结构。
也可以通过层序遍历来做。
# 代码
空想起来感觉会挺复杂,但实际代码倒是比较简短,多看几遍熟悉下吧hhhh
前序遍历:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.flag = -1
def Serialize(self, root):
# write code here
if not root:
return '#,'
return str(root.val)+','+self.Serialize(root.left)+self.Serialize(root.right)
def Deserialize(self, s):
# write code here
self.flag += 1
l = s.split(',')
if self.flag >= len(s):
return None
root = None
if l[self.flag] != '#':
root = TreeNode(int(l[self.flag]))
root.left = self.Deserialize(s)
root.right = self.Deserialize(s)
return root
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
层序遍历:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
"""Encodes a tree to a single string.
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: str
"""
r = []
q = []
q.append(root)
while q:
root = q.pop(0)
if root:
r.append(str(root.val))
q.append(root.left)
q.append(root.right)
else:
r.append('#') # 空节点
r.append(' ') # 换层
return ''.join(r)
def deserialize(self, data):
"""Decodes your encoded data to tree.
:type data: str
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
tree = data.split()
if tree[0] == '#': #空节点
return None
q = []
root = TreeNode(int(tree[0]))
q.append(root)
i = 1
while q:
cur = q.pop(0)
if not cur:
continue
cur.left = TreeNode(int(tree[i])) if tree[i] != '#' else None
cur.right = TreeNode(int(tree[i+1])) if tree[i+1] != '#' else None
i += 2
q.append(cur.left)
q.append(cur.right)
return root
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
# 天际线问题
Leetcode 218题
# 问题
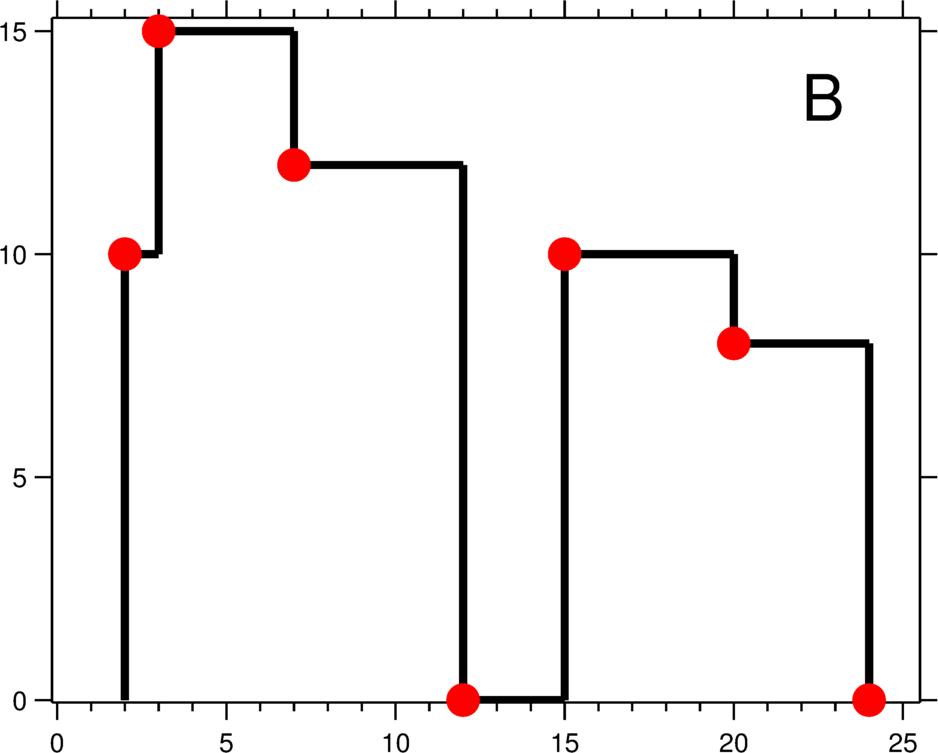
城市的天际线是从远处观看该城市中所有建筑物形成的轮廓的外部轮廓。现在,假设您获得了城市风光照片(图A)上显示的所有建筑物的位置和高度,请编写一个程序以输出由这些建筑物形成的天际线(图B)。
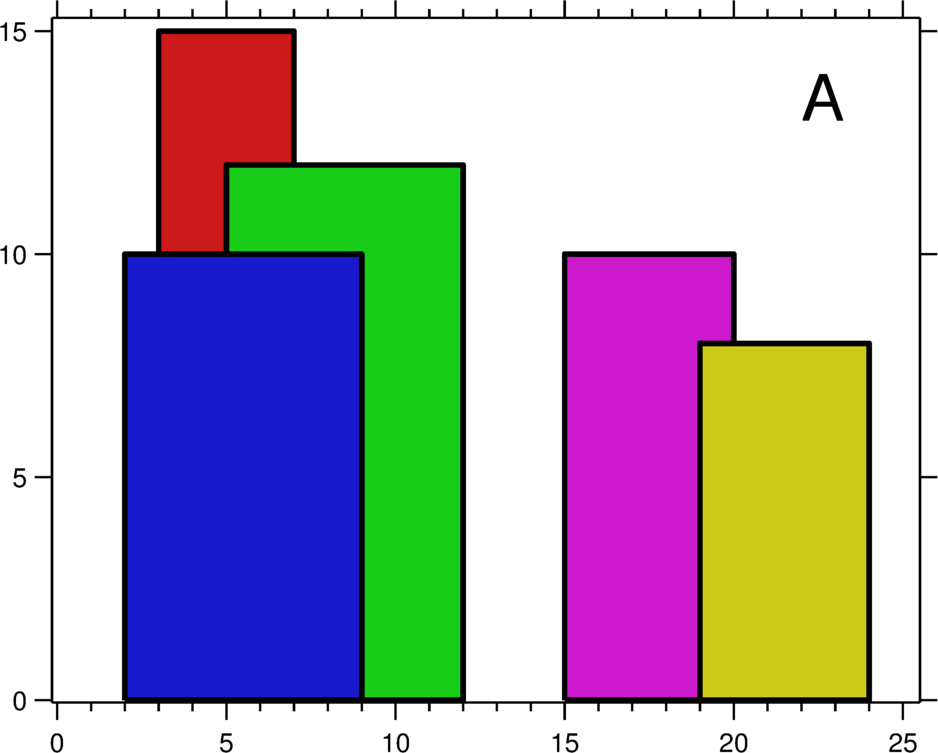
每个建筑物的几何信息用三元组[Li,Ri,Hi]表示,其中 Li 和 Ri 分别是第 i 座建筑物左右边缘的 x 坐标,Hi 是其高度。可以保证 0 ≤ Li, Ri ≤ INT_MAX, 0 < Hi ≤ INT_MAX 和 Ri - Li > 0。您可以假设所有建筑物都是在绝对平坦且高度为 0 的表面上的完美矩形。
例如,图A中所有建筑物的尺寸记录为:[ [2 9 10], [3 7 15], [5 12 12], [15 20 10], [19 24 8] ]。
输出是以 [ [x1,y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], ... ]格式的“关键点”(图B中的红点)的列表,它们唯一地定义了天际线。关键点是水平线段的左端点。请注意,最右侧建筑物的最后一个关键点仅用于标记天际线的终点,并始终为零高度。此外,任何两个相邻建筑物之间的地面都应被视为天际线轮廓的一部分。
例如,图B中的天际线应该表示为:[ [2 10], [3 15], [7 12], [12 0], [15 10], [20 8], [24, 0] ]。
说明:
- 任何输入列表中的建筑物数量保证在 [0, 10000] 范围内。
- 输入列表已经按左 x 坐标 Li 进行升序排列。
- 输出列表必须按 x 位排序。
- 输出天际线中不得有连续的相同高度的水平线。例如 [...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...] 是不正确的答案;三条高度为 5 的线应该在最终输出中合并为一个:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
# 思路
这个是hard难度的题,乍一看也确实没啥清晰思路2333。这里记录一个找到的思路吧。
关键是要找出高度发生变化的点。所以首先我们用一个list来存储所有给出的建筑物信息,包含建筑物的两个端点及其高度,这些端点就是将来可能会高度发生变化的点。为了便于区分起点终点以及后面的排序,我们将建筑起点的高度记为负值,终点高度记录为正数。
然后对列表进行排序,优先按照横轴坐标从左往右排序,横轴坐标相同的,按照纵轴高度排序。
接下来初始化一个最大堆,堆顶是当前建筑轮廓的最高高度,遍历上面的list,对每个元素,如果这个点是起点,则要将它(的值变回正值)加入堆中,如果是一个终点,则要将它从堆中移出,操作完之后判断下堆顶的高度是否发生了变化,如果发生变化,则说明这个点是一个高度变化的点,我们将这个点和当前高度加入到结果集中。
# 代码
按照上面的思路,可以写出如下代码。注意,python中使用了heapq来实现堆,但是最小堆,我们采用将所有元素取负值的方式利用最小堆来实现最大堆,所以在【1】的地方有一点特殊的实现逻辑。
import heapq
class Solution(object):
def getSkyline(self, buildings):
"""
:type buildings: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not buildings or not buildings[0]:
return []
# 构建列表
coors = []
for b in buildings:
coors.append((b[0], -b[2]))
coors.append((b[1], b[2]))
# 列表排序
coors.sort(key=lambda x: (x[0], x[1]))
# 开始遍历
data = []
res = []
pre, cur = 0, 0
heapq.heappush(data, 0)
for c in coors:
# 【1】本该是将负值变为正值进堆,但heapq是小根堆,所以这里是将正值变为负值进堆,这样堆的最小值取负之后就是实际的最大值
if c[1] < 0:
heapq.heappush(data, c[1])
else:
data.remove(-c[1]) # 【2】
heapq.heapify(data)
cur = -1 * data[0]
if cur != pre:
res.append([c[0], cur])
pre = cur
return res
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
很可惜的是这个方法在leetcode上没有通过,原因是在【2】处,没有提供从堆中移除某个元素的方法,所以只好手动从列表中移除元素,然后重建堆。而leetcode中有一个很长的用例,这个方法就超时了。
下面是来自leetcode的另外方法,有不同的思路,首先将所有起止点的横坐标加入列表,对列表进行排序,将来我们就只考虑这些点就可以,因为肯定是在这些点才会有机会发生转折。
然后对边界点列表进行循环。
import heapq
class Solution(object):
def getSkyline(self, buildings):
# 把左边界和右边界的横轴坐标保留下来
x = [i[0] for i in buildings] + [i[1] for i in buildings]
# 排序
x.sort()
index = 0
heap = []
res = [[0, 0]]
# 从小到大的顺序循环边界的值
for i in x:
# 先来判断这个点是不是左边界,如果是左边界,则把对应的建筑加入堆中。
# index表示的是建筑的编号,找到建筑左边界等于i的建筑放到大根堆
# (这里看似是while,但其实每个建筑只被处理了一次,因为x是按照从小到大排的,buildings也是按照左边界从小到大排的,所以没有问题~
while index < len(buildings) and buildings[index][0] == i:
# 大根堆存放的是(高,右边界)
heapq.heappush(heap, (-buildings[index][2], buildings[index][1]))
# 建筑编号加1
index += 1
# 大根堆的堆顶元素即建筑的最高值
# 来判断下这栋建筑的右边界,如果右边界小于等于i,即该建筑已经遍历完了,不需要了,则从堆中移出,依次类推
while heap and heap[0][1] <= i:
heapq.heappop(heap)
# 如果堆里仍然有值,把堆顶的元素的高取出来就是当前点的最高
h = -heap[0][0] if heap else 0
# 和结果中的高进行对比,如果不相同,说明不在一条直线上,把该值添加到res中
if h != res[-1][1]:
res.append([i, h])
return res[1:]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34